The consumer sometimes needs additional amounts (Amendments) added to their bill due to reasons from outside of the system. The addition of amounts happens with respect to the consumer code of the entity in the product(PT, WS, etc..,), any unpaid demand in the system is a candidate for amendments.
Prior knowledge of billing-service in the DIGIT framework.
Amendment mainly works with two types of functionality as follows:
Amendment
Demand
Bill Amendment provides a separate flow that triggers the workflow for validating the process of adding additional amounts to existing demands. This validation was earlier available only to the respective modules. An amendment is allowed only when there is a need to add or reduce the amount from the existing bill belonging to an entity. The reasons for such cases could be:
Court case settlement
One time waiver
Write-offs
DCB correction (old demands in paid status)
Property tax remission
Criteria:
Below are certain prerequisites to creating an amendment,
presence of demand in the billing system
any one of the reasons listed above
valid document proof for the reason
there is no other amendment already in the workflow
Procedure:
The process of adding an amendment in specific scenarios is given below.
There are two scenarios on how an amendment is completed based on the paid status of the existing demands in the system.
1. when demand is unpaid/partially paid
Create a demand (Or an existing demand can be used) with demand detail → DD1.
Do not pay the bill or make a partial payment.
Create an amendment for the same consumer code (with demand detail → DD2).
Approve the amendment - the response should return an amendment with the status CONSUMED.
Search the demand or fetch the bill for the consumer code. The demand/bill should contain demand details of the demand and amendment together with DD1 and DD2 in the same demand/bill.
2. when demand is completely paid
Create demand and make complete payment or choose a consumer code which is fully paid.
Create amendment (with demand detail → DD1).
Approve amendment - the response should be APPROVED.
Create new demand for the consumer code (with demand detail → DD3). The demand response should contain two demand details DD1 and DD2 saved to the demand.
The amendment search returns CONSUMED status after the demand is created.
IMPACT: Does not impact any other functionality other than adding demand details to demands on APPROVAL.
IMPACTED BY: Existence of demands in the system.
Billing Service | Configuration-Details: Refer to billing-service config for MDMS data. The amendment makes use of the same data set.
WORKFLOW CONFIG:
Amendment integration helps organizations add additional value to the demand without any change in the system.
Easy to create and simple process of updating demands
Helps ease changes into the system which are not part of normal functionality - Amendment of bills in case of legal requirements.
This is integrated into the billing system by default.
The amendment facility can be used in case of a legal issue to add values to existing demands using /amendment/_create. The parameter /amendment/_update is used to cancel the created updates or update configured workflows.
{yet to be added}
API Definition
API List
/amendment/_create, _update
The main objective of the billing module is to generate the bill for all revenue-based business services. To serve the bill, the Billing-Service requires demand. Demands will be prepared by the revenue modules and stored by billing based on which it generates the Bill.
Prior Knowledge of Java/J2EE.
Prior Knowledge of Spring Boot.
Prior Knowledge of KAFKA
Prior Knowledge of REST APIs and related concepts like path parameters, headers, JSON, etc.
Prior knowledge of demand-based systems.
The following services should be up and running:
user
MDMS
Id-Gen
URL-Shortening
notification-sms
eGov billing service creates and maintains demands.
Generates bills based on demands.
Updates the demands from payment when the collection service takes a payment.
Deploy the latest image of the billing service available.
In the MDMS data configuration, the following master data is needed for the functionality of the billing.
MDMS
Business Service JSON
TAX-Head JSON
Tax-Period JSON
Billing service can be integrated with any organization or system that wants a demand-based payment system.
Easy to create and simple process of generating bills from demands
The amalgamation of bills period-wise for a single entity like PT or Water connection.
Amendment of bills in case of legal requirements.
Customers can create a demand using the /demand/_create
Organizations or Systems can search the demand using /demand/_searchendpoint
Once the demand is raised the system can call /demand/_update endpoint to update the demand as per need.
Bills can be generated using, which is a self-managing API that generates a new bill only when the old one expires /bill/_fetchbill.
Bills can be searched using /bill/_search.
Amendment facility can be used in case of a legal issue to add values to existing demands using /amendment/_create and /amendment/_update can be used to cancel the created ones or update workflow if configured.
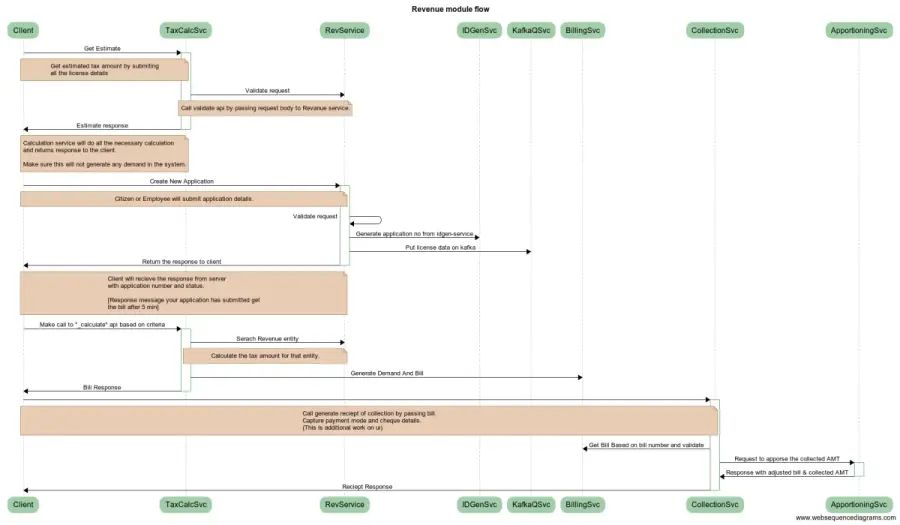
Interaction Diagram V1.1:
Doc Links
API List
What is apportioning?
Adjusting the receivable amount with the individual tax head.
Types of apportioning V1.1
Default order-based apportioning(Based on apportioning order adjust the received amount with each tax head).V1.1
Types of apportioning V1.2: (TBD)
Proportionate-based apportioning (Adjust total receivable with all the tax heads equally)
Order & percentage-based apportioning (Adjust total receivable based on order and the percentage which is defined for each tax head).
Principle of apportioning
The basic principle of apportioning holds that if the full amount is paid for any bill then each individual tax head should get nullified with their corresponding adjusted amount.
Example: Case 1: When there are no arrears all tax heads belong to their current purpose.
Example: given below
Case 2: Apportioning with two years of arrear: Example: The apportioning details for the financial year 2014-15 are given below.
The table below illustrates the demand structure generated in case there are no payments for the specified financial year (2015-16).
All content on this page by eGov Foundation is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
All content on this page by is licensed under a .
bs.businesscode.demand.updateurl
Each module’s application calculator should provide its own update URL. if not present then a new bill will be generated without making any changes to the demand.
bs.bill.billnumber.format
BILLNO-{module}-[SEQ_egbs_billnumber{tenantid}]
IdGen format for the bill number
bs.amendment.idbs.bill.billnumber.format
BILLNO-{module}-[SEQ_egbs_billnumber{tenantid}]
is.amendment.workflow.enabled
true/false
enable disable workflow of bill amendment
Id-Gen service
****
url-shortening
MDMS
/demand/_create, _update, _search
/bill/_fetchbill, _search
/amendment/_create, _update
Pt_tax
1000
6
1000
1000
750
750
AdjustedAmt
1000
-250
-750
-750
RemainingAMTfromPayableAMT
0
0
0
0
Penality
500
5
500
500
AdjustedAmt
500
-500
RemainingAMTfromPayableAMT
1000
250
Interest
500
4
500
500
AdjustedAmt
500
-500
RemainingAMTfromPayableAMT
1500
750
Cess
500
3
500
500
AdjustedAmt
500
-500
RemainingAMTfromPayableAMT
2000
1250
Exm
-250
1
-250
-250
AdjustedAmt
-250
250
RemainingAMTfromPayableAMT
2250
1750
Rebate
-250
2
-250
-250
AdjustedAmt
-250
250
RemainingAMTfromPayableAMT
2500
750
Pt_tax
1000
2014
2015
6
Current
AdjustedAmt
0
Penality
500
2014
2015
5
Current
AdjustedAmt
0
Interest
500
2014
2015
4
Current
AdjustedAmt
0
Cess
500
2014
2015
3
Current
AdjustedAmt
0
Exm
-250
2014
2015
1
Current
AdjustedAmt
0
Pt_tax
1000
2014
2015
6
Arrear
AdjustedAmt
0
Pt_tax
1500
2015
2016
6
Current
AdjustedAmt
0
Penalty
600
2014
2015
5
Arrear
AdjustedAmt
0
Penalty
500
2015
2016
5
Current
AdjustedAmt
0
Interest
500
2014
4
Arrear
AdjustedAmt
0
Cess
500
2014
3
Arrear
AdjustedAmt
0
Exm
-250
2014
1
Arrear
AdjustedAmt
0